cbasspy.mapManipulations package¶
Submodules¶
cbasspy.mapManipulations.beam2bl module¶
-
PnX(l, x)¶
-
beam2bl_I(beam, theta, lmax, xtheta=True, calc_err=False)¶ Calculates the Legendre Transform of an I beam. Uses the integrator in
cbasspy.mapManipulations.integrateand the recurisve relationships between Legendre polynomials.Parameters: beam : array_like
Array of beam values.
theta : array_like
Corresponding array of theta values.
lmax : int
Maximum l you want to calculate the Legendre Transform to.
xtheta : optional {True,False}
Set to True if you want to use theta as the x variable, False to use cos(theta).
calc_err : optional, {True,False}
Set to True if you want to calculate an estimate of the truncation error. Note this has not been well tested, in particular the calculation of the 6th order derivative of the integrand!
Returns: ell : array_like
0 to lmax.
window : array_like
The window function at each ell.
err : float, optional
Truncation error estimate.
See also
beam2bl_P- Equivalent function but for polarization window functions.
-
beam2bl_P(beam, theta, lmax, xtheta=True, calc_err=False)¶ Function for calculating the spin-2 Legendre Transform of the beam. Uses the integrator in
cbasspy.mapManipulations.integrate, and the recurisve relationships between Legendre polynomials and their derivatives.Parameters: beam : array_like
Array of beam values.
theta : array_like
Corresponding array of theta values.
lmax : int
Maximum l you want to calculate the Legendre Transform to.
xtheta : optional, {True,False}
Set to True is you want to use theta as the x variable, set to False to use cos(theta).
calc_err : optional, {True,False}
Set to True if you want to return an estimate of the truncation error. Note this has note been tested well, particularly the calculation of the 6th derivative of the integrand!
Returns: ell : array_like
0 to lmax
window : array_like
The spin-2 window function at each ell
err : float, optional
Estimate of the truncation error (optional)
See also
beam2bl_I- Equivalent function but for total intensity window functions.
cbasspy.mapManipulations.beam2bl_I module¶
-
beam2bl_I(beam, theta, lmax, xtheta=True)¶ Calculates the Legendre Transform of an I beam. Uses the integrator in integrate.py and the recurisve relationships between Legendre polynomials.
Required arguments: beam - Array of beam values. theta - Corresponding array of theta values. lmax - Maximum l you want to calculate the Legendre Transform to.
Optional arguments: xtheta - True/False. Set to True if you want to use theta as the x variable,
False to use cos(theta).- calc_err - True/False. Set to True if you want to calculate an estimate of the truncation error.
- Note this has not been well tested, in particular the calculation of the 6th order derivative of the integrand!
Returns: ell - 0:lmax window - the window function at each ell err - truncation error estimate (optional)
History: 15/02/2018 - RG Created 16/02/2018 - LJ Removed plotting 26/02/2018 - RG Added truncation error estimates
cbasspy.mapManipulations.beam2bl_P module¶
-
beam2bl_P(beam, theta, lmax, xtheta=True, calc_err=False)¶ Function for calculating the spin-2 Legendre Transform of the beam. Uses the integrator in integrate.py, and the recurisve relationships between Legendre polynomials and their derivatives.
Required arguments are:
- beam - Array of beam values.
- theta - Corresponding array of theta values.
- lmax - Maximum l you want to calculate the Legendre Transform to.
Optional arguments:
- xtheta - True/False. Set to True if you want to use theta as the x variable, False to use cos(theta).
- calc_err - True/False. Set to True if you want to return an estimate of the truncation error. Note this has note been tested well, particularly the calculation of the 6th derivative of the integrand!
Returns:
ell - 0:lmax window - The spin-2 window function at each ell err - Estimate of the truncation error (optional)
cbasspy.mapManipulations.deconvolveMap module¶
-
createN2S(inMap, ell, doPol=True, ellMin=10.0, ellMax=100.0, spice_name='spice_TEB_spectra.txt', temp_signal_name='_temporaryDeconv_IQU_signal.fits')¶ Function to estimate the noise-to-signal ratio as a function of ell. The noise level is determined from the 10th from last element in the signal spectrum. The signal level is determined from a straight line fit to log(Cl)/log(ell) in the range [ellMin:ellMaxx]. The noise-to-signal ratio is retured at ell
Parameters: inMap : array_like
Input healpix sky map
ell : array_like
Multipole moments to return the N2S ratio at
doPol : bool, True
Whether to do T or TEB
ellMin : float, 10.
Lower bound of ell range to fit signal straight line to
ellMax : float, 100.
Upper bound of ell range to fit signal straight line to
spice_name : str, ‘spice_TEB_spectra.txt’
Name of spice parameter file to use, it looks in the cbasspy/mapManipulations directory.
temp_signal_name : str, ‘_temporaryDeconv_IQU_signal.fits’
What to save a temporary map as in the current working directory.
Returns: N2S : array_like
Array of noise-to-signal ratios. Either TT or [TT,EE,BB]
-
createWindowsFromRimo(rimo_file_name, fwhm, windowFileName, ext_name='BEAMWF_030X030', saveWindowFns=True, extend_ell=False, extend_ell_max=2048)¶ - Load the beam Bls from a Planck RIMO file and create the window functions required to
deconvolve to a Gaussian beam. If the output is saved to a file then it can be loaded in by
deconvolveMap()Parameters: rimo_file_name : str
Name of Planck RIMO fits file
fwhm : float
Gaussian beam to smooth to [radians]
windowFileName : str
Name of file to save window functions to. The saved files have the format [windowFileName]I.txt and [windowFileName]P.txt
ext_name : str, ‘BEAMWF_030X030’
Name of fits extension containing beam Bls
saveWindowFns : optional {True, False}
Whether to save the window functions so that they can be loaded in the future
Returns: ell : array_like
Multipole moments
inBeamBl_I : array_like
Input Planck beam
inBeamBl_P : array_like
Input Planck beam, note this is the same as inBeamBl_I
outBeamBl_I : array_like
Gaussian beam to smooth to
outBeamBl_P : array_like
Gaussian beam to smooth to
ratio_I : array_like
alm reweighting function
ratio_P : array_like
alm reweighting function
-
createWindowsFromTxt(txt_file_name, fwhm, windowFileName, saveWindowFns=True, extend_ell=False, extend_ell_max=2048)¶ Load the beam Bls from a WMAP txt file and create the window functions required to deconvolve to a Gaussian beam. If the output is saved to a file then it can be loaded in by
deconvolveMap()Parameters: txt_file_name : str
Name of WMAP txt file
fwhm : float
Gaussian beam to smooth to [radians]
windowFileName : str
Name of file to save window functions to. The saved files have the format [windowFileName]I.txt and [windowFileName]P.txt
ext_name : str, ‘BEAMWF_030X030’
Name of fits extension containing beam Bls
saveWindowFns : optional {True, False}
Whether to save the window functions so that they can be loaded in the future
Returns: ell : array_like
Multipole moments
inBeamBl_I : array_like
Input Planck beam
inBeamBl_P : array_like
Input Planck beam, note this is the same as inBeamBl_I
outBeamBl_I : array_like
Gaussian beam to smooth to
outBeamBl_P : array_like
Gaussian beam to smooth to
ratio_I : array_like
alm reweighting function
ratio_P : array_like
alm reweighting function
-
deconvolveMap(inMap, theta, beam, fwhm, NSIDE_out, niter=3, inCov=None, returnLots=False, saveWindowFns=False, loadWindowFns=False, windowFileName='windowFunctions', inMapCoord='c', useDecMask=False, outMapCoord='g', cutMin=-90, cutMax=0, numOfNoiseSims=3, doTapering=False, ell_min=200, ell_max=2000, doWiener=False, dgUsingAlms=False)¶ Function to deconvolve a map, smooth to fwhm and downgrade to NSIDE_out.
Parameters: inMap : array_like
Input map to be smoothed, in Ta (antenna temperature). Shape (npix,) or (n,npix)
theta : array_like
Array of angles at which the beam is sampled in radians
beam : array_like
Beam profile at each angle
fwhm : float
Gaussian beam to smooth to [radians]
NSIDE_out : int
Nside to downgrade output map to
niter : int, optional {3}
Number of iterations when estimating alms from map
inCov : array_like, optional {None]
Covariance map, if None then not used. Should take one of three forms [cov(I)] or [cov(I),cov(Q),cov(U)] or [cov(I),cov(Q),cov(U),cov(IQ),cov(IU),cov(QU)] and have shape (npix,), or (3,npix) or (6,npix). Note that the covariances are not used, only the variances.
returnLots : optional, {False,True}
If False, only returns smoothed map If True, also returns ell, inBeamBl, outBeamBl, ratio, omega_beam and omega_out
saveWindowFns : optional {True,False}
Whether to save the window functions so that they can be loaded in the future
loadWindowFns : optional {True,False}
whether to load in window functions from txt file. NOTE, this overrides theta, beam and fwhm given earlier
windowFileName : str, optional, {‘windowFunctions’}
Name of file to save window functions to or to load them from The saved files have the format [windowFileName]I.txt and [windowFileName]P.txt
useDecMask : optional, {True,False}
Whether to apply a declination mask the the smoothed and downgraded map
inMapCoord : str, optional {‘C’,’G’,’E’}
The coordinate system of the input map.
outMapCoord : str, optional {‘C’,’G’,’E’}
The coordinate system to rotate the map to.
cutMin : float, optional {-90}
The minimum declination to cut in degrees.
cutMax : float, optional {0}
The maximum declination to cut in degrees.
numOfNoiseSims : int, optional {3}
The scaling factors for the smoothed variance maps are estimated from simulated realisations of the noise. This integer determines how many simulations to use.
doTapering : optional {False,True}
Whether to apply a cosine taper to the window function.
ell_min : int, optional {200}
When to begin the tapering.
ell_max : int, optional {2000}
When to finish tapering.
doWiener : bool, False
Whether to do wiener deconvolution. See
createN2S()and the How To doc. for details.dgUsingAlms : bool, False
If True, downgrade Nside on E and B maps, not Q and U maps. No effect if just I map.
Returns: outMap : array_like
Smoothed and downgraded maps. Has shape (npix_out,) or (3,npix_out)
outVarMap : array_like
Smoothed and downgraded variance maps. Has same shape as outMap.
If inCov was None, then this is also None.
outVarMapScaleFactor : float
This should be appllied to outVarMap to correct for smoothing and downgrading. Has shape (1) or (3).
ell : array_like, optional
Multipole moments of the window functions.
inBeamBl_I : array_like, optional
I beam window function
inBeamBl_P : array_like, optional
P beam window function
outBeamBl_I : array_like, optional
I outbeam window fuction
outBeamBl_P : array_like, optional
P outbeam window function
ratio_I : array_like, optional
alm reweighting function in I. If doWiener==True then this includes the Wiener weighting.
ratio_P : array_like, optional
alm reweighting function in P. Note, if doing a Wiener deconvolution then E and B have different N2S ratios and are treated separately.
omega_beam : float, optional
in beam solid angle [radians]
omega_out : float, optional
outbeam solid angle [radians]
ratio_E : array_like, optional
Only returned if (returnLots==True)&(doWiener==True) The reweighting function accounting for Wiener filtering
ratio_B : array_like, optional
Only returned if (returnLots==True)&(doWiener==True) The reweighting function accounting for Wiener filtering
N2S : array_like, optional
Only returned if (returnLots==True)&(doWiener==True) The noise-to-signal estimates for TT (and EE and BB if polarization is turned on)
-
interp_kink(window_file, lmin, lmax, no_ell, pol, save_window=False, window_out_dir='.', create_plot=False, plot_out_dir='.')¶ Function for removing the kink in the C-BASS window function, replacing it with a smooth interpolated function between lmin and lmax.
Returns: ell: The input ells. numpy.ndarray
new_bl: The new beam bl’s, with the smoothed kink. numpy.ndarray
gl: The input Gaussian window. numpy.ndarray
new_rl: The new window function ratio, with the smoothed kink. numpy.ndarray
-
rotateMap(inMap, inCov, incoord, outcoord)¶ Wrapper to rotate map and variance map.
Parameters: inMap : array_like
Input map, can have shape [npix,3], [npix,]. If shape [npix,3] then assumes [Imap,Qmap,Umap]
inCov : array_like
Input covariance map. Can have shape [npix,3], [npix,]
incoord : str, {‘E’,’C’,’G’}
Coordinate system of input map
outcoord : str, {‘E’,’C’,’G’}
Coordinate system of output map
Returns: outMap : array_like
Rotated map
outCov : array_like
Rotated covariance map
-
smoothVarMap(inVar, ratio, dgUsingAlms=False, dgAlmNside=64)¶ Reweights the variance map in alm space with ratio and does the same to a realisation of the noise.
Parameters: inVar : array_like
Variance maps either var(I) with shape (npix,) or [var(I),var(Q),var(U)] with shape (3,npix). e.g., inVar = np.array([inCov[0],inCov[1],inCov[2]])
ratio : array_like
alm reweighting functions, with shape (lmax+1,) if just I or (3,lmax+1) if I,Q and U. e.g., ratio = np.array([ratio_I,ratio_P,ratio_P])
dgUsingAlms : book, False
If True, downgrade during alm2map else don’t downgrade
dgAlmNside : int, 64
The Nside to downgrade to
Returns: outVarMap : array_like
smoothed var map with same shape as inVar
outNoiseMap : array_like
smoothed noise realisation map with same shape as inVar
-
taperFn(ell, ell_min, ell_max)¶ Calculate a cosine taper function.
Parameters: ell : array_like
ell values at which to evalutate the taper.
ell_min : int
where the cosine taper starts.
ell_max : int
where the cosine taper ends.
Returns: taper : array_like
Taper function evaluated at l values in ell.
cbasspy.mapManipulations.integrate module¶
This module is used to numerically integrate tabulated data using the Newton-Cotes method of arbitrary order.
i.e. it is an approximation to 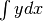 .
.
Although these functions live in cbasspy.mapManipulations they will likely find use outside of this context!
-
integrateData(x, y, order, return_err=False)¶ Integrates y over the x range, splitting the data up into intervals of length order and using the Newton-Cotes method on the intervals.
Parameters: x : array_like
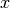 -ordinates.
-ordinates.y : array_like
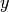 -absicia
-absiciaorder : int
Maximum length of data to integrate in one go.
return_err : optional, {True,False}
Return the average error coefficient if True.
Returns: integral : float
Integral of y over the x range.
error : float
Average error coefficient. (optional)
See also
integrateInterval- The Newton-Cotes integration function.
-
integrateInterval(x_sub, y_sub)¶ Integrates y_sub over the range of x_sub, using the newton_cotes method. Will fail if length of data is too long.
This is called by
cbasspy.mapManipulations.integrateData(). Usually you will want to call the integrate function, rather than this one.Parameters: x_sub : array_like
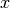 -ordinates
-ordinatesy_sub: array_like
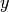 -absicia
-absiciaReturns: integral : float
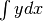 over the range of
over the range of 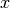 .
.error : float
Newton-Cotes error coefficient.
See also
integrateData- A function that calls this in a sensible way.
cbasspy.mapManipulations.pix_QU_rot module¶
-
pix_rotate_QU(vec1, vec2, Q, U)¶ This code calculates the rotation in the local coordinate axes defining Q and U at the position defined by the vector vec1, when rotating to the position given by the vector vec2. The subsequent transformation in Q and U is then calculated.
This can be compared to the global QU rotation code, where we consider the change in Q and U across the whole sky under the action of some global coordinate change.
Parameters: vec1 : array_like, [3,]
Position of the original pixel centre, described by unit vector vec1.
vec2 : array_like, [3,]
Position of the final pixel centre, decribed by unit vector vec2.
Q : float
The Q value in the pixel specified by vec1.
U : float
The U value in the pixel specified by vec2.
Returns: Qprime : float
The Q value in the parent pixel, specified by vec2.
Uprime : float
The U value in the parent pixel, specified by vec2.
Notes
The angle-axis rotation matrix between vec1 and vec2 is given by:
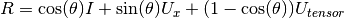
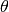 - angle of rotation about the Euler axis.
- angle of rotation about the Euler axis.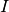 - Identity matrix.
- Identity matrix.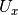 - Cross matrix of vector u, the unit vector defining the Euler axis/
- Cross matrix of vector u, the unit vector defining the Euler axis/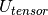 - Tensor product of the vector u.
- Tensor product of the vector u.
There are an infinite number of rotation matrices that can map from one vector to another, we have just chosen a convenient form.
cbasspy.mapManipulations.rotate_QU module¶
Module for rotating I, Q and U maps in pixel space.
-
rotate_ang_QU(Qmap, Umap, alpha, beta, gamma)¶ This code rotates the Q and U maps, given a set of Euler angles defining the rotation.
Parameters: Qmap : array_like
The input HEALPix Q map, in the input coordinate system.
Umap : array_like
The input HEALPix U map, in the input coordinate system.
alpha : float
The first Euler angle, in degrees (rotation counterclockwise around original Z).
beta : float
The second Euler angle, in degrees (rotation counterclockwise around interim Y).
gamma : float
The third Euler angle, in degrees (rotation counterclockwise around final X).
Returns: Qrot_map : array_like
Rotated Q map
Urot_map : array_like
Rotated U map
See also
rotate_coord_QU- Rotate Q and U maps between different coordinate systems.
-
rotate_coord_I(inmap, incoord, outcoord, interpEdgeValue=-5.0)¶ Script to rotate an I map in pixel space Performs rotation by interpolating onto new map.
Parameters: inmap : array_like [npix,]
Total intensity HEALPix map
incoord : str {‘e’,’c’,’g’}
Coordinate system of input map
outcoord : str {‘e’,’c’,’g’}
Coordinate system of output map
interpEdgeValue : float, {-5.0}
The interpolation can cause strange results near the edge of the map. Anything smaller than this value after rotation will be set to the UNSEEN value.
Returns: rotatedMap : array_like
HEALPix map rotated to new coordinate system.
See also
rotate_coord_QU- Rotate Q and U maps between different coordinate systems.
-
rotate_coord_QU(Qmap, Umap, incoord, outcoord, isVarMap=False)¶ This code calculates the rotation of Q and U, at the position of some vector in input coordinates, under the rotation from the input to output coordinates (i.e. what happens to the orientation of the local coordinate axes defining Q and U when we change from the input to output coordinates, and apply the corresponding rotation to Q and U).
Parameters: Qmap : array_like
Input HEALPix Q map, in the input coordinate system.
Umap : array_like
Input Healpix U map, in the input coordinate system.
incoord : str, {‘E’,’C’,’G’}
The input coordinate system.
outcoord : str, {‘E’,’C’,’G’}
The output coordinate system.
isVarMap : optional, {False,True}
Are the input Q and U maps variance maps?
Returns: Qrot_map : array_like
Rotated Q map.
Urot_map : array_like
Rotated U map.
See also
rotate_coord_I- Rotate I map between coordinate systems.
rotate_ang_QU- Rotate Q and U maps using Euler angles.